Hints of Alien Life: Scientists Look to Washington and Oregon Coast
Published 04/10/2019 at 5:33 AM PDT
By Oregon Coast Beach Connection staff
Includes exclusive listings; some specials in winter
In Cannon Beach:
Includes rentals not listed anywhere else
In Manzanita, Wheeler, Rockaway Beach:
Some specials for winter
In Pacific City, Oceanside:
Some specials for winter
In Lincoln City:
Some specials for winter
In Depoe Bay, Gleneden Beach:
Some specials for winter
In Newport:
Look for some specials
In Waldport
Some specials for winter
In Yachats, Florence
Some specials for winter
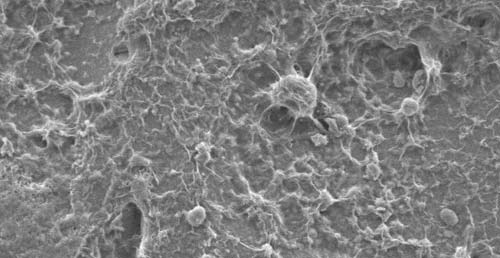
(Corvallis, Oregon) – Scientists from Oregon State University in Corvallis recently published their findings regarding microbial life off the Washington coast that are not only more primitive than previously known to exist but they also help give glimpses into what life on other worlds may be like.
With their ship docked in Astoria, on the north Oregon coast, researchers dug down 1.6 miles below the surface of the ocean off the Juan de Fuca Ridge, about 120 miles off the coast of Washington’s Olympic Peninsula. There, they discovered a form of microbe so unevolved it resembles the lifeforms of Earth’s earliest existence. It was a remarkable discovery: a community of hydrogen-consuming microbes that were like nothing seen before.
In their paper, the researchers reveal a community of microbial organisms that survives using an ancient metabolic method that is so unlike most other lifeforms currently in existence.
OSU’s Amy Smith was a doctoral student at the time, and she’s now lead author on the paper recently published in the ISME Journal, a publication of the International Society for Microbial Ecology. In it, she describes an organism with a very different metabolism, one that has not evolved since life first popped up on this planet billions of years ago.
“We went into the study expecting to find one kind of microbe, and we found others - similar, but a more ancient lineage dependent upon hydrogen,” Smith said.
It’s the sort of find that has some in the astronomy world excited as well: these kinds of extremophiles (microbes that thrive in extremely hot environments) are of interest to those looking for life on other planets. Scientists at OSU said these “may be the type of life most likely to exist on any of a billion planets that contain water and volcanic rock.”
The project took a few years. Researchers drilled deep holes into basalt rock – reaching down more than 1100 feet below the ocean floor – then placed PVC plastic chambers inside. Leaving these “traps” for four years, the microbes eventually colonized the minerals inside. They found at least 11 different species of primitive microbes.
These creatures live without oxygen, according to another OSU researcher on the project, Martin Fisk. Instead of living on organic carbon, they eat hydrogen. It’s believed they existed at a time when Earth had no oxygen.
It’s likely even the Oregon coast has these tiny time-trippers lurking offshore.
“We believe these microbes are actually throughout all of oceanic crust, which covers over 60 percent of the Earth’s surface,” Smith said. “They especially love it hot, so crust that is covered in sediment helps keep their habitat the perfect temperature. The sediment that covers the area we studied came from the continents originally either as runoff or as algae and diatoms bloomed near the coast. This area is susceptible to glacial-interglacial cycles and sea level changes due to its proximity to land. I would say it could be considered a near-shore spreading ridge that is affected by continental processes.”
Oregon Coast Lodgings in this area - Where to eat - Maps - Virtual Tours
Cannon Beach Lodging
Nehalem Bay Lodgings
Manzanita Hotels, Lodging
Three Capes Lodging
Pacific City Hotels, Lodging
Lincoln City Lodging
Depoe Bay Lodging
Newport Lodging
Waldport Lodging
Yachats Lodging
Oregon Coast Vacation Rentals
Oregon Coast Lodging Specials
More Oregon coast below:




More About Oregon Coast hotels, lodging.....
More About Oregon Coast Restaurants, Dining.....
LATEST Related Oregon Coast Articles
A petition on procedural matters denied; no major changes yet. Whale
Oceanfront Kitchettes in Seaside, Near Gearhart, Near Cannon Beach
Large rooms right up against the surf and Promenade. Watch for whales as you prepare a meal. Seaside reviews, hotel reviews, specials
Slightly Rare: Fin Whale Washes Up on N. Oregon Coast - and They Knew It Was ...
Only 3 others have washed up since 2002; this one near Seaside, Gearhart. Video. Marine sciences
China Creek Access (#155) at Bandon: Between South Oregon Coast Wonders
A sandy expanse between Face Rock and Cape Blanco. Travel tips
ODFW Implements Changes Aimed at Cutting Chances of Whale Entanglement Off Or...
Late season rules for commercial crabbing now a month earlier. Marine sciences
Oregon Coast This Week: Grisly 'Globster' Stuck in Devil's Punchbowl, Rescue ...
A whale carcass is floating around Devil's Punchbowl; an injured hiker was rescued at Bayocean. Marine sciences
The Opposite of an Exploding Whale: Oregon Coast History of 'Zombie Whales'
1952: whale would not stay buried. Was it finally entombed in cement. Marine sciences
Forecasts for Oregon Coast Whale Watch Week, How Well It Cooperates
Chilly and windy at times but mostly calm waves that let you spot them. Weather
Oregon Coast Whale Watch Week Comes as Scientists Worry About Latest Populati...
Saturday, Dec. 27 through Wednesday, Dec. 31 from Brookings to Warrenton. Brookings events, Gold Beach events, Port Orford events, Coos Bay events, Bandon events, Florence events, Yachats events, Newport events, Lincoln City events, Rockaway Beach events, Manzanita events, Cannon Beach events, Seaside events, Astoria events
Oregon Coast's Crabbing Fleet Heads Out with Whale Entanglement Advisory
Environmental groups petition ODFW for greater whale safety measures. Marine sciences
Investigation of Young Whale Incident on Oregon Coast Already Makes New Finds
Commercial crabbing gear was a part after all, among other findings. Marine sciences
Latest on Oregon Coast Humpback Whale: Rescue Fails, Euthanized
Officials: stay away from this site in north Yachats. Marine sciences
Stranded and Struggling Humpback Whale on Central Oregon Coast Draws Crowds O...
Experts warn stay away from the Yachats site. Dozens try to help but endanger themselves. Marine sciences
55 Years of 'Happy Exploding Whale Day' Celebrated in Oregon Coast's Florence
Nov 12 is the holiday, but Florence's celebrates Nov 16. Florence events, south coast events, Newport events
Back to Oregon Coast
Contact Advertise on BeachConnection.net
All Content, unless otherwise attributed, copyright BeachConnection.net Unauthorized use or publication is not permitted